#Oxford Medical Simulation
Text
Denmark: A significant healthtech hub

- By InnoNurse Staff -
According to data platform Dealroom, Danish healthtech firms raised a stunning $835 million in 2023, an 11% rise over the previous record set in 2021.
Read more at Tech.eu
///
Other recent news and insights
A 'Smart glove' could improve the hand movement of stroke sufferers (The University of British Columbia)
Oxford Medical Simulation raises $12.6 million in Series A funding to address the significant healthcare training gap through virtual reality (Oxford Medical Simulation/PRNewswire)
PathKeeper's innovative camera and AI software for spinal surgery (PathKeeper/PRNewswire)
Ezdehar invests $10 million in Yodawy to acquire a minority stake in the Egyptian healthtech (Bendada.com)
#denmark#startups#innovation#smart glove#stroke#neuroscience#iot#Oxford Medical Simulation#health tech#digital health#medtech#education#pathkeeper#ai#computer vision#surgery#ezdehar#yodawy#egypt#mena
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Metaverse and Healthcare: Innovations in Virtual Health Services

In the ever-evolving digital landscape, a transformative force is reshaping the healthcare ecosystem – the metaverse. This boundless virtual realm, powered by cutting-edge technologies like virtual reality (VR) and artificial intelligence (AI), promises to revolutionize how we deliver medical services and facilitate innovative treatment modalities.
Imagine a world where geographical barriers cease to exist, where patients can access world-class healthcare from the comfort of their homes, and where medical professionals can hone their skills in realistic virtual environments before ever stepping into an operating room. This is the future that the metaverse is ushering in, and it's a future that promises to redefine the very essence of healthcare delivery.
At the forefront of this revolution are virtual consultations and remote patient monitoring. By leveraging immersive VR technologies, healthcare providers can conduct virtual appointments with patients, enabling real-time visualization and collaboration regardless of physical location. This not only improves accessibility but also enhances the quality of care by providing a richly detailed and interactive environment for diagnosis and treatment.
Renowned institutions like the Cleveland Clinic are already pioneering these virtual healthcare capabilities. In partnership with Pixeleyes, the Cleveland Clinic has created a virtual medical campus, enabling remote learning and collaboration among healthcare professionals worldwide. This groundbreaking initiative is paving the way for a future where expertise can transcend geographical boundaries, ensuring that patients have access to the best possible care, no matter where they are located.
Beyond consultations, the metaverse offers a revolutionary platform for medical training and education. Through advanced VR simulations, healthcare professionals can practice complex procedures in a risk-free digital environment, honing their skills and gaining invaluable experience without jeopardizing patient safety. Oxford University's Medical Virtual Reality (OVMR) program is a prime example of this, utilizing cutting-edge VR technologies to train medical students in various clinical scenarios, fostering a safe and immersive learning environment.
The metaverse's potential extends far beyond training and consultations. In the realm of mental health care, virtual reality exposure therapy (VRET) is emerging as a powerful treatment modality for conditions such as anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and phobias. By recreating controlled virtual environments, therapists can gradually expose patients to triggering situations, helping them develop coping mechanisms and overcome their fears in a safe and controlled digital space.
As transformative as these current applications are, the metaverse's impact on healthcare is merely the beginning. Future iterations will leverage advanced AI capabilities for automated diagnosis and treatment plan recommendations, revolutionizing the way we approach personalized medicine. Furthermore, the integration of blockchain technology will facilitate the secure sharing of comprehensive virtual medical records, empowering patients with true data ownership while introducing new layers of trust and transparency to healthcare infrastructure.
While the adoption of the metaverse in healthcare is still in its early stages, the potential benefits are undeniable. By bridging the gap between physical and virtual healthcare delivery, the metaverse promises to improve access to quality care, enhance training opportunities, and facilitate innovative treatment approaches that were once confined to the realm of science fiction.
However, as we navigate this uncharted territory, it is crucial for healthcare providers, technology companies, and policymakers to collaborate and address ethical and regulatory challenges. Addressing privacy concerns, defining legal boundaries, and future-proofing policies will ensure that the metaverse transforms healthcare responsibly and ethically, benefiting all stakeholders in the process.
The healthcare industry stands at the precipice of a digital revolution, and those who embrace the metaverse early will be at the forefront of this transformation. By harnessing the power of immersive technologies and virtual worlds, we can unlock new frontiers in patient care, medical education, and groundbreaking treatments, ushering in a new era of healthcare where the boundaries between reality and possibility are blurred.
Embrace the Future of Healthcare, Embrace the Metaverse.
0 notes
Text
Virtual Training and Simulation Market Will Hit Big Revenues In Future | Biggest Opportunity Of 2024
The virtual training and simulation is the combination where training is conducted in a virtual or simulated environment when the learner or the trainee and the instructor are in separate locations. Virtual training can be done synchronously or asynchronously, it gives the traditional classroom or learning experience. The simulation helps learners to believe that the settings are real and they can act or respond to it by making mistakes and actually doing no harm or wastage leading to the real-time learning experience. This technology is widely used in various industries including education, healthcare, military for training students, medical trainees, and military troops respectively. Currently, virtual training and simulation are being used in training nursing students for clinical learning in the wake of COVID-19.
Free Sample Report + All Related Graphs & Charts @: https://www.advancemarketanalytics.com/sample-report/100306-global-virtual-training-and-simulation-market?utm_source=Organic&utm_medium=Vinay
Latest released the research study on Global Virtual Training and Simulation Market, offers a detailed overview of the factors influencing the global business scope. Virtual Training and Simulation Market research report shows the latest market insights, current situation analysis with upcoming trends and breakdown of the products and services. The report provides key statistics on the market status, size, share, growth factors of the Virtual Training and Simulation The study covers emerging player’s data, including: competitive landscape, sales, revenue and global market share of top manufacturers are CAE Inc (Canada), The DiSTI Corporation (United States), Oxford Medical Simulation (United States), SimforHealth (MediActiv) (France), Elbit Systems Ltd., (Israel), VirtaMed AG (Switzerland), Mursion Inc. (United States), Kratos Defense & Security Solutions, Inc. (United States), Cubic Corporation (United States), Virtro (Canada)
Thanks for reading this article; you can also get individual chapter wise section or region wise report version like North America, Europe or Southeast Asia.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Excel in NEET with Pune's Premier Repeater Coaching Classes
Introduction
The National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (NEET) is one of the most competitive and challenging examinations in India. Every year, thousands of students aspire to secure a seat in prestigious medical colleges across the country, making NEET preparation a paramount task. For many, the journey to NEET success requires multiple attempts, and that's where NEET repeater coaching classes in Pune come into play. In this article, we will explore the significance and benefits of joining these specialized coaching classes, and why Pune is emerging as a hub for NEET repeater students.
The Need for NEET Repeater Coaching
Securing a good rank in NEET is crucial for students aspiring to become doctors and pursue a career in medicine. However, not all students manage to clear this challenging examination on their first attempt. This is where NEET repeater coaching classes prove to be indispensable. They cater specifically to students who are giving NEET another shot, ensuring they are equipped with the right strategies, study material, and guidance to improve their performance.
Why Pune for NEET Repeaters?
Pune, often referred to as the "Oxford of the East," is renowned for its educational institutions and vibrant academic culture. It is fast becoming a preferred destination for NEET repeater coaching for several reasons:
1. Experienced Faculty: Pune boasts a pool of experienced and knowledgeable faculty members who are well-versed in the NEET syllabus and exam pattern. These teachers are experts in their respective fields and can provide the right guidance to repeater students.
2. Competitive Environment: Pune is home to numerous NEET repeater coaching centers, attracting students from all over India. This competitive environment encourages students to push their limits and strive for excellence.
3. Access to Resources: Pune offers easy access to a plethora of educational resources, including libraries, study materials, and online platforms. This facilitates a comprehensive and structured study approach.
4. Strategic Location: Pune's strategic location in western India ensures easy connectivity to major cities and towns in the region. This makes it convenient for students coming from different parts of the country.
5. Supportive Community: The presence of a large community of NEET aspirants and repeaters in Pune fosters a sense of camaraderie and support. Students can exchange ideas, share resources, and motivate each other throughout their preparation journey.
Benefits of NEET Repeater Coaching in Pune
1. Customized Study Plans: Repeater coaching classes in Pune offer customized study plans tailored to the specific needs of each student. This helps in addressing weaknesses and focusing on areas that require improvement.
2. Regular Mock Tests: These coaching classes conduct regular mock tests that simulate the NEET examination environment. These tests help students gauge their progress, identify areas of improvement, and build their confidence.
3. Comprehensive Study Material: Pune's coaching centers provide comprehensive study material, including textbooks, practice papers, and reference materials. These resources are meticulously curated to cover the entire NEET syllabus.
4. Personalized Attention: With smaller batch sizes, NEET repeater coaching classes in Pune can provide personalized attention to each student. This ensures that doubts are cleared promptly and individual progress is closely monitored.
5. Experienced Mentors: Repeater coaching classes in Pune often have mentors who are themselves successful NEET repeaters or medical professionals. Their guidance and mentorship can be invaluable in motivating students and providing insights into the medical profession.
6. Time Management Skills: NEET repeater coaching in Pune helps students develop effective time management skills, which are crucial for attempting a time-bound examination like NEET.
7. Emphasis on Concept Clarity: These coaching classes focus on building a strong foundation of concepts in subjects like Physics, Chemistry, and Biology. This not only helps in NEET but also in future medical studies.
8. Psychological Support: Preparing for NEET again can be mentally challenging. NEET repeater coaching classes in Pune often provide psychological support and counseling to help students cope with stress and anxiety.
Conclusion
NEET repeater coaching classes in Pune have emerged as a beacon of hope for students who wish to give their dreams of becoming a doctor another chance. With a plethora of benefits, experienced faculty, and a competitive environment, Pune offers the ideal ecosystem for NEET repeaters to thrive. These coaching classes not only equip students with the necessary knowledge and skills but also instill confidence and determination to excel in the NEET examination. So, if you are a NEET repeater, consider Pune as your destination for a brighter future in the field of medicine.
0 notes
Text
Metaverse: The next frontier for Health 4.0

With a predicted market size of USD 800 billion by 2024, the metaverse is taking social connections to the next level. Over 74% of adults in the US have joined or are considering joining this virtual space. Various industry experts have discussed how the metaverse can transform gaming, entertainment, socializing, work, and commerce. However, not a lot has been spoken about how it might affect healthcare.
Metaverse involves the convergence of three major technological trends — artificial intelligence (AI), augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR). Together, they can open up completely new channels for delivering treatment, lowering costs, and significantly improving patient outcomes in healthcare.
Three major channels fuelling the use of metaverse in healthcare
1. Telemedicine
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the use of telemedicine gained a lot of traction, as before that only 43% of healthcare facilities could deliver remote therapy to patients. That percentage has now risen to 95%. Metaverse will supplement telemedicine visits with a virtual office, where patients and physicians can meet in a 3D clinic or any other location.
This is projected to improve the user experience for teleconsultation services significantly. Using VR, the metaverse in healthcare can enable next-level immersion, by providing a considerably higher sense of “being there” than other virtual environments like websites, messaging applications, or social media. Through such consultations, patients will no longer be restricted to being treated by specific specialists owing to their physical location. It’s particularly valuable in places like China, where medical personnel are in poor supply, as well as for patients in distant areas who would otherwise have to travel a long way to visit a doctor.
Therapy is another area where the metaverse in healthcare can be highly effective. Patients can interact with situations that cause them anxiety in safe environments where every aspect of the interaction can be closely monitored and controlled. For instance, gameChange, a virtual reality system developed by Dr. Daniel Freeman and his colleagues at the University of Oxford is using VR to treat psychosis using a form of medical technology known as digital therapeutics or DTx.
A scene from the gameChange VR system: Simulation of a doctor’s waiting area

2. Blockchain
Blockchain is a critical part of the metaverse in healthcare, according to experts, because it allows for decentralized communities controlled democratically via smart contracts, as well as a record of digital “ownership” of environments or even items in the digital world. The management and security of our highly valuable health data is blockchain’s most prominent use case in healthcare.
Currently, data is frequently transferred between many companies in an inefficient and opaque manner in the eyes of the data’s owners. Because health records are typically maintained on centralized computers, our information is vulnerable to theft (a single health record is reported to be worth between USD 70 and USD 100 on the dark web). It also means that obtaining it, even for those who have a valid need for it – such as a professional who is treating us – can be a time-consuming and exhausting process.
3. Digital twins
A digital twin is a virtual model or simulation of any object, process, or system that is created using real-world data to learn more about its real-world counterpart. In the metaverse, the patient’s digital twin could be the patient themself.
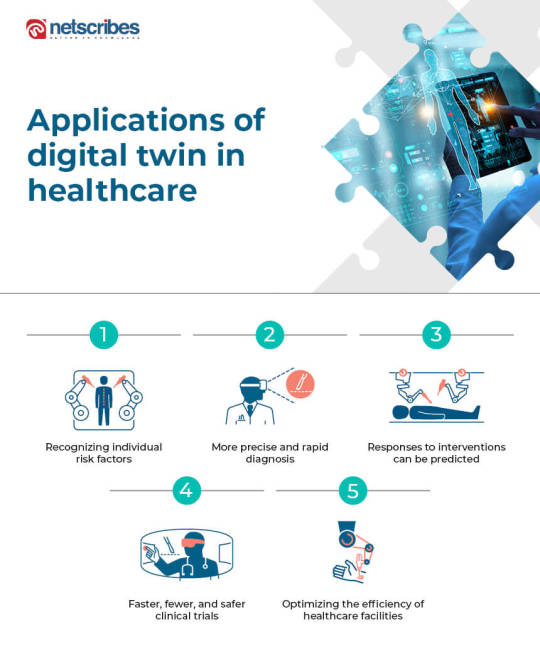
Digital twins, according to Jack Latus, CEO of Latus Health, an online healthcare service specialized in occupational health, will eventually be used as “test dummies” for individuals, predicting everything from how we will recover from surgery to how we would react to specific medicines. This will develop further when our ability to map and comprehend individual genetics improves.
Consider a virtual representation of a single person where every known medicine for that person’s illness can be tested. This will allow the best treatment to be determined. It can even monitor the virtual “person” and notify you if a medical condition develops as a side-effect enabling preventive actions. Many large med-tech companies, such as Siemens Healthineers and GE Healthcare, are working on digital twins. To achieve their goal, these companies will require critical assets including massive amounts of patient data.
A sneak peek at the future of metaverse in healthcare
Making things easier for patients
With the convergence of these core technologies in the metaverse – clinicians will be able to provide more integrated treatment programs and packages, devoid of the siloed nature of much of the current healthcare system. These technologies-based solutions are already enhancing patient experiences and outcomes. Even simple procedures like intravenous injections and blood draws can benefit from them, for instance, through using Accuvein, a technology that casts a map of a patient’s veins onto the skin.
Recently, med-tech giant Medtronic acquired AI-powered surgical platform Digital Surgery, and Zimmer Biomet also introduced its new OptiVu Mixed Reality system, which uses the Microsoft HoloLens to integrate the real and virtual worlds. With such major investments in med-tech being made to leverage the metaverse, along with a growing number of startups creating AR and VR solutions, the surgical environment will soon witness radical transformation in the next few years.
Facilitating collaboration among healthcare professionals
The ability to immediately share information between healthcare professionals would allow for quicker identification of the underlying causes of illness. Monitoring patient activity in the metaverse also allows for easier tracking of variables like compliance, which will aid in the diagnosis and treatment of illnesses.
Veyond Metaverse, for example, is also bringing together worldwide healthcare professionals for concurrent education, training, and planning, as well as collaborative medical operations. It uses innovative cloud and real-time communication technology to “empower doctors to practice their skills with the highest accuracy to ensure everyone receives the best healthcare service anytime and wherever,” according to the company’s website.
There is a possibility that the metaverse in healthcare will fundamentally alter and improve the industry over the next few years. Despite the optimism, there are still various obstacles on the path to standardizing metaverse in healthcare, including the adoption of smart technologies, particularly among the elderly population. Healthcare companies will also need to develop a new business model that is connected with patient health insurance, reimbursements, and prescriptions, all in this new virtual space.
However, these limitations will be accompanied by an essentially boundless user experience, breaking down geographical constraints and creating limitless possibilities for patients all over the world.
Netscribes’ healthcare insights solutions help organizations drive growth through a deeper understanding of their customers, disruptive technologies, and the market as a whole.
0 notes
Text
Global Virtual Training and Simulation Market is set to Fly High Growth in Years to Come
Latest added Virtual Training and Simulation Market research study by AMA Research offers detailed outlook and elaborates market review till 2027. The market Study is segmented by key regions that are accelerating the marketization. At present, the market players are strategizing and overcoming challenges of current scenario; some of the key players in the study are CAE Inc (Canada)
The DiSTI Corporation (United States)
Oxford Medical Simulation (United States)
SimforHealth (MediActiv) (France)
Elbit Systems Ltd., (Israel)
VirtaMed AG (Switzerland)
Mursion Inc. (United States)
Kratos Defense & Security Solutions, Inc. (United States)
Cubic Corporation (United States)
Virtro (Canada) etc.
The virtual training and simulation is the combination where training is conducted in a virtual or simulated environment when the learner or the trainee and the instructor are in separate locations. Virtual training can be done synchronously or asynchronously, it gives the traditional classroom or learning experience. The simulation helps learners to believe that the settings are real and they can act or respond to it by making mistakes and actually doing no harm or wastage leading to the real-time learning experience. This technology is widely used in various industries including education, healthcare, military for training students, medical trainees, and military troops respectively. Currently, virtual training and simulation are being used in training nursing students for clinical learning in the wake of COVID-19.
Influencing Trend: Rising Use of Virtual Training and Simulation in Medicine and Healthcare Industry
Demand for Virtual Training and Simulation in Manufacturing Industry for Precise Designing and Production of the Product
Challenges: Stringent Regulatory Compliance with Virtual Training and Simulation
Opportunities: Growing Spendings of Various Industries in Virtual Training and Simulation
Surging Demand for Virtual Training and Simulation in Military and Defense
Market Growth Drivers: The Demand for Engaging, Appealing and Immersive Technology
Growing Demand for the Virtual Environment that Mimics Real-life Use in Various IndustryThe Global Virtual Training and Simulation segments and Market Data Break Down by Application (Virtual Schools, Institutes, Hospitals, Others), Components (Hardware, Software, Service), Platform (Computer, Smartphones, VR Devices), Industry Verticals (Healthcare Industry, Education Industry, Gaming Industry, Entertainment Industry, Manufacturing Industry, Others)
Presented By
AMA Research & Media LLP
0 notes
Text
Artificial Intelligence: A Guide for Thinking Humans
AI has been one of the hottest topics for more than two or three generations and it still creates buzz around the world. Some of the world’s brightest minds believe AI will take the human race to the next stage of evolution. It's a topic that requires great attention if not taken care properly, then it can cause catastrophic changes to the human race. The ability of AI exceeds far more than we can imagine, and it still fascinates me how vast AI could grow. There isn’t any limit to its capabilities.
Here the discussion is about how people from different generations viewed AI and their assumptions or perspective regarding AI. What stages of evolution did AI go through?
What challenges did they face on their course of action? How far is AI from reaching human-level potential? It also discusses AI’s lack of generalization or understanding of real-life situations. The potential of what AI could grow or evolve into and when these things can be achieved are discussed here. The danger that lies ahead in the development of AI is also mentioned here.
In 1958 one of the first AI systems that learned from training examples was created. It attempts to automate intelligence by using inspiration from the brain. It was developed by Frank Rosenblatt, who tried to simulate how neurons work and also how simple networks of neurons recognize perceptual input. The greatest minds of AI during the 1960s firmly believed that they would see human-level AI within the next 10 to 20 years and also, and they had a dream which was to address issues such as natural language understanding, computer vision, and so on. They believed that these things could be achieved in a short amount of time. According to Melanie Mitchell AI is an umbrella term that includes computational methods for getting things done that we consider intelligent. And what was considered intelligence at one point in time had changed over the course of time. With programmes such as IBM’s deep blue which had beaten world chess champions, the idea of intelligence had also changed over the course of time. There was also another belief in AI that instead of focusing on learning, our focus should be more on humans trying to program in knowledge and rules that the system uses. To illustrate with an example, an expert system that gained high popularity during the 1970s and 1980s would conduct interviews with experts in medical diagnosis. They would extract these experts’ knowledge and rules and later programme them into the computer. Many of the rules and knowledge extracted from these experts were general knowledge or common knowledge of how the world worked as these were used without conscience and as a result, it turned out to be a great disappointment. People struggled a lot more while working in AI in the past than today. They didn’t get much support as well as funding and there was a lot of disbelief in its success. Even today, they don’t give accurate results when the variables in an equation change. The results are also affected by this.
Guest: Melanie Mitchell
Melanie Mitchell is a well-known American scientist. She currently holds the position as the Davis professor of complexity at the Santa Fe Institute. Her area of expertise includes analogical reasoning, complex systems, complex systems, genetic algorithms, and cellular automata, and her publication in these respective fields has gained attention widely. She was awarded her Ph.D. from the University of Michigan under the guidance of Douglas Hofstadter and John Holland. She published six books and various scholarly papers in the areas of artificial intelligence, cognitive science, and complex systems. She was honored by Oxford Press University for her book “Complexity: A Guided Tour” and was also considered one of the best science books of 2009 by Amazon.com. Artificial Intelligence: A Guide for Thinking Humans is her latest creation. She created Santa Fe Institute’s Complexity Explorer Platform, which provides online courses and educational resources in the area of complex systems. More than 25,000 enrolled in her online course program “Introduction to Complexity” and holds a position in one of the top 50 online courses of all time in Course Central.
References:
0 notes
Photo
Virtual Reality is awesome for gaming and entertainment but it is also great for more serious applications. A great example is Oxford Medical Simulation. 🥽🏥🥼 @oxfordmedicalsimulation With the ongoing disruption from COVID-19, colleges and universities are increasingly cancelling some or all in-person classes. OMS offers distance-learning solutions using VR with multiple scenarios and virtual patients. Check Oxford Medical Simulation on the Instagram tag above. Follow me: 🤖@RobotsPlayingGames Thank you! RPG: Robots Playing Games 🤖💜🕹️ ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ ------Robots-Playing-Games------ #healthcare #oxford #medical #simulation #game #gamer #gaminglife #gamers #videogame #videogames #gamestagram #instagame #instagamer #nostalgia #fun #nintendo #playstation #xbox #play #retrocollective #photooftheday #gaming #videogameaddict #games #gamersofinstagram #instagramers #retrogaming #retrogamer #retrogames #playinggames https://www.instagram.com/p/B_IHva0nRLh/?igshid=yyo5b2fsvmem
#healthcare#oxford#medical#simulation#game#gamer#gaminglife#gamers#videogame#videogames#gamestagram#instagame#instagamer#nostalgia#fun#nintendo#playstation#xbox#play#retrocollective#photooftheday#gaming#videogameaddict#games#gamersofinstagram#instagramers#retrogaming#retrogamer#retrogames#playinggames
0 notes
Text
Dark academia dress guide for the medical student
I will celebrate that I have officially ended my first semester of medical school by writing this post (also kind of procrastinate studying for my winter exams, oops), since now I have 18 weeks of experience on dressing for college.
Mind you, how a medical student dresses in first and second year IS WILDLY different from how you dress in third, fourth, fifth and sixth year. In the first couple of years you spend most of your time in college, doing labs, attending lectures, going to the dissection room, and at most going to health centers and psychiatric wards to shadow physicians, and that’s only in select colleges. Starting third year you will spend more time in the hospital and simulation centers wearing uniform scrubs and lab coats than in a regular lecture hall, although, sometimes your rotation will mandate you wear casual business clothes.
That said, dark academia outfits for every occasion in the first year of medical school, plus practicality tips:
For the regular lecture day: wear comfortable high waisted pants, (maybe colored mom jeans, cigarette pants, belted pants, culottes) or a high waisted skirt, maybe a midi or a pencil one. You can wear a button up blouse, a turtleneck in winter, comfortable wool sweaters, etc. For summer, flowy dresses and skirts, loose blouses in silk, linen or cotton. Always, always, always carry a cardigan or a blazer or both BECAUSE IT GETS SO COLD IN LECTURE HALLS. Go with layers in winter and autumn and spring. For shoes, ankle boots in black or brown leather that’s a bit worn, ballet flats, loafers, I love those you can lace up your ankle, oxfords, lace up boots. Mostly comfortable shoes. Leave a good impression with your lecturer because that’s your future colleague right there.
If you will stay in the library until late hours studying, wear comfortable pants. I think you could make drawstring pants dark academia if they are high waisted, kinda loose but follow the line of your body, and if you wear them with a button up loose blouse or turtleneck or sweater, a blazer and boots or ballet flats depending on the weather.
For days you have to stay until 8 pm because you have a lab or a seminar, you can wear what you wore on lecture days unless it’s something to do with an actual lab with chemicals, like biology, biochemistry, and anatomy labs. In that case: your white lab coat, wear flat and close toe shoes that are comfortable because you will spend a long time on your feet. Such a long time on your feet. Ballet shoes, in this case, are not recommended. Boots are best, oxfords are fine. Make sure your shoes are made of something you can whipe off. Getting formaline and bits of dead people is hard to erase on canvas shoes. Also, don’t wear frilly things to the labs, no skirts or long dresses either. Wear shirts with short sleeves or that you can fold up. Wear the typical dark academia pants mentioned above. Be comfortable. For the people with long hair: wear it up and away from your face, no sweet romantic pieces falling on your head, channel Mary Curie and wear a bun, a braided crown, or a high ponytail. Never ever ever wear shorts, they will not let you in the lab.
I want to add: the last three weeks I spent everyday going to the dissection room until they closed at night to study for my anatomy practical exam and let me tell you: dress in layers when you have to go to that room because it is always cold, like a fridge, but you have to wear the lab coat on top. Wear your hair up, maybe a French twist? Also, always take your dissection kit with you because a fellow classmate will ask you to help them analyze a biological piece and you might need your tweezers and such.
For exams: dress well, smart and comfortable. I make a lot of emphasis for comfort because you will spend long hours in college absorbing a lot of information that will later save lives, and you deserve to be comfortable. For oral exams it is essential you dress well and leave a good impression with your examiner, everything counts. For written exams dress like you would for a lecture or the library because those are long.
For hospital and health center visits: unless you have to wear scrubs, you should wear the formal version of lecture outfits. In general, dark academia fashion is very conservative and professional, you look serious and profound, so great job dressing well. Just wear comfortable shoes, dress pants, and a button down or turtleneck, plus a pristine version of your white coat (don’t take the one you use for anatomy because it is dirty and it smells and it is likely stained). Wear your hair up if you it long.
Makeup for med school: I’d say something minimal, a dark lip and mascara. I think that dark under eye circles add to the aesthetic so no need to conceal those unless you want to. Maybe winged eyeliner, mascara and pink lips. Wear some blush high on your cheeks and the tip of your nose for that cold flushed look. Do your eyebrows well, that’s essential. Wear some burgundy eyeshadow on your eyelids if you want, or a color that truly brings out your eyes. Highlighter if you want to look ethereal and haunting, which is always a great thing. Curl your eyelashes. Wear sunscreen!
Accessories: a golden locket around your neck, a small ring or rings. Honestly: get small rings, big rings you have to remove every single time you need to put on rubber gloves. A bracelet with charms, and teardrop earrings or pearls. I’d say with jewelry the most important thing is that the color of your metals match: gold with gold and silver with silver. Avoid rose gold and copper pieces, those look too banal. Wear a head band on your head, or ribbons. Lots of ribbons. Get a nice leather dissection kit but make sure your pieces are always held securely, otherwise when you want to remove something and they are loose you can cut yourself and that’s no fun. Always carry some books on your arms to look smart. Solid color scarves are great for winter, as well as leather gloves, and a beret or classic earmuffs. For summer, a silk scarf with a French knot, sunglasses. Looser, thinner fabrics, but same cut of clothes. No turtlenecks, or sweaters naturally. Boatneck shirts in a solid color with pants or skirts are always elegant. You, again, can wear drawstring pants if you use the formula stated above. Same makeup as before. Take a picnic blanket in your bag to have a picnic on the grass with your friends or to study under an ancient tree.
#dark academia#dark aesthetic#dark academic aesthetic#medical#med school#studyblr#outfit#dark academia outfit#light academia#light acadamia aesthetic#studyspiration#studyspo
47 notes
·
View notes
Text
Could AI render human labour in all fields useless?
What is Artificial Intelligence; What is it used for and what is the impact?
AI or Artificial Intelligence is the theory and development of computer systems to be able to perform tasks and jobs that normally requires human intelligence. For example: visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, etc. -Oxford Dictionary
Artificial intelligence has a myriad of uses such as:
Non player characters in video games
Stock market trading bots
Content filters on social media
Autopilot on an aeroplane
Self-Driving cars
Artificial Intelligence is also being used in extremely experimental ways. One of these cases is Watson by IBM. Watson had made an appearance on television beating people at the game show Jeopardy, but his directive is to learn how humans express medical issues in their own words and try to give an accurate diagnosis. He has already gotten a start by trying to diagnose lung cancer patients.
This topic has been extremely relevant in recent years due to the ever increasing speed of innovation in the modern world. There have been countless tests proving time and time again that AI is better and could eventually become better than human physical and mental labour. This topic has been talked about by many authoritative figures (Elon Musk, Stephen Hawking, Bill Gates, etc). There have been politicians discussing it but only one is doing something about it. Andrew Yang is an American presidential candidate who is taking a unique political side on AI. He is taking in relevant information from trusted sources and he is proposing a solution called UBI (universal basic income). He proposes that due to AI taking away jobs from many in the US that he is giving a ‘freedom dividend’ of $1000 per American citizen every month to allow our capitalist society to continue with a high unemployment through no fault of their own.
How does artificial intelligence work?
Artificial intelligence is a broad term for a lot of different algorithms but the main branch that is associated with ‘taking over jobs’ is machine learning. The way machine learning works is that you give the algorithm data and an operation on what to do with that data. They begin analysing it and teach themselves the relationships between the data and how to complete the task at hand. This principal is most notably found in online retail. Amazon for example gets its algorithms to analyse the data you produce on their website and these algorithms produce a list of items you are more likely to purchase and they then recommend them to you.
History of Artificial Intelligence
The concept of living machines that act like humans has been around ever since the ancient Greeks but artificial intelligence was not officially named as such until 1956 at a conference at Dartmouth College in New Hampshire where the term artificial intelligence was coined by John McCarthy who is credited as one of the founding fathers of AI along with Alan Turing, Marvin Minsky and Herbert A. Simon. -Washington University
But proper funded research did not begin until the 1960’s when the Department of Defence funded various research efforts and there were various other laboratories that appeared across the world. Herbert Simon was extremely optimistic about the future of AI stating “machines will be capable, within twenty years, of doing any work a man can do”. But during the 70’s research had slowed down a lot due to some unexpected issues with creating a well performing set of artificial neurons. These issues were spotted by Sir James Lighthill. But they were corrected.
By the 1980’s artificial intelligence has received a resurgence in popularity and investment because of the creation of expert systems which are a branch of ai which can simulate/replicate the knowledge and skill of humans. By 1985 the market of AI had reached 1 billion USD. Simultaneously in Japan they were developing the ‘fifth generation computer system’ which sparked some intrigue for the UK and the US so they began to fund further research into AI.
In the 1990’s and early 2000’s AI was being used more frequently for things such as video game NPC’s and the stock market (as I have previously mentioned). The reason for the success and popularity is the increasing power of computers and the increasing availability of them. In 1997 an AI program called deep blue was the first chess playing AI to beat a reigning champion.
Why AI will not take our jobs
Artificial intelligence and automation has proven to be very effective and efficient in low-skilled, repetitive jobs. But in recent years there has been an ever increasing concern that artificial intelligence will advance so quickly that it will be able to complete white collar jobs such as those in an office. While it’s easy to get scared and worry about the security of your job we first have to look at the research and facts. The World Bank’s Development report of 2019 pushes the idea forward that, while automation displaces workers it creates just as many jobs to balance the situation and allow them to continue to earn money and keep the economy growing. According to the report the total Labour Force has been increasing ever since 1993.
Figure 0.4 World Bank’s World Development Report
The traditional office has changed dramatically over the past fifty years. For instance people are not accounting by calculating with a calculator and a piece of paper they have software to do this for them. This does not mean that the software has replaced their job, it has just improved the way they work. Automation and computerisation has made things easier, ever increasingly scaleable quicker and more productive. Artificial intelligence is not taking away from people’s jobs, it’s either improving them or giving them the opportunity to modify their skill set to suit other industries that AI will create.
Why AI will take our jobs
The development of artificial intelligence can be classified in three different waves, the first wave was the attempt to develop general intelligence comparable to a human, the second wave was the development of expert systems which aid in small scale decision making such as medical diagnoses and the third wave is the development of machine learning. -source 1
There are many fields where AI is being implemented but finance is one of the most prominent as businesses would like to turn a profit from their investments. These AI algorithms can also: reduce costs, minimise risks, prevent fraud, verify borrowers and evaluate their solvency, as well as make predictions and perform other tasks for the company they work for.
The main focus of the AI finance developments are the stock market. Instead of somebody hiring a trained market evaluator they can just purchase an AI algorithm which in a lot of cases works more effectively at looking at the state of the market giving you the best companies to invest in.
An example of this is a study by Eureka-hedge where they gave 23 hedge funds to human investors and 23 hedge funds to AI for investment. The funds given to the investors gave an annual increase (yield) of a range of 1.62% to 2.62% meanwhile the AI gave an annual yield of 8.44%. The researchers contribute this fact to the AI constantly repeating testing of the market rather than accumulating data like humans do.. -Eureka Hedge (From source1)
Artificial intelligence is implemented in many other other ways as well such as creating other AI algorithms. Google’s AI system learned how to create other machine learning algorithms better and make them more efficient than human created ones. The test for the created algorithms was image identification. The AI trained algorithm was able to 43% of the objects it was tasked to identify in the image whereas the human created AI was only able to identify 39% of them.
Google’ CEO Sundar Pichai had this statement at a presentation in 2017 saying that AI does not fully replace humans currently but allows more people to be able to “develop” AI. -
“Today these are handcrafted by machine learning scientists and literally only a few thousand scientists around the world can do this. We want to enable hundreds of thousands of developers to be able to do it.”
-Wired AI creating AI better than humans
Another way AI is beating humans is in the legal field. A study conducted by LawGeex was to compare AI to 20 lawyers who worked for companies such as Goldman Sachs and Cisco and they had dozens of years of experience working for these companies. Their task was to evaluate the risks contained in five different Non Disclosure Agreements and identify 30 specific legal points.
From the results we can see that the AI system showed an average accuracy of 94% while the lawyers average was 85%. The maximum accuracy for the AI 100% while the lawyers was 94%. The average time taken by the lawyers was 92 minutes, the AI’s was 26 seconds
-LawGeex Lawyers v. AI
Finally the last case study is where AI can be better than humans in the medical field. This study was to test the accuracy of Pap tests for cancerous signs.
Mark schniffman. Senior editor : Our findings show that a deep learning algorithm can use images collected during routine cervical cancer screening to identify precancerous changes that, if left untreated, may develop into cancer. In fact, the computer analysis of the images was better at identifying precancer than a human expert reviewer of Pap tests under the microscope (cytology).
In general, the algorithm worked better than all standard screening tests in predicting all cases diagnosed in the Costa Rica-based study. Automatic visual assessment revealed precancerous disease with greater accuracy (AUC = 0.91) than human examination (AUC = 0.69) or conventional cytology (AUC = 0.71). An AUC value of 0.5 indicates a test that is no better than a random one, while an AUC value of 1.0 represents a test that has perfect accuracy in detecting disease. From these results we can deduce that humans do not
This Graph shows how likely each profession is to be automated
Source: https://www.economist.com/graphic-detail/2018/04/24/a-study-finds-nearly-half-of-jobs-are-vulnerable-to-automation
As you can see, low skill jobs such as construction, cleaning, driving and garment manufacturing are at high risk of automation. Jobs that require human emotion and connection such as hospitality, upper management and politics and teaching are extremely unlikely as robots cannot socialise and recognise emotions.
This graph details the level of automation that the OECD predicts in each country in the near future.
As you can see 43 percent of irish jobs are susceptible to becoming automated. This figure is largely dependent upon which sector of the economy your country has the majority employed in. For example countries with a lot of low skilled primary economic activities such as farming or forestry are going to have a higher percentage of automated employment. The highest percentage of automation is Slovakia and the Lowest is New Zealand
My opinion:
Artificial intelligence will and is currently eliminating jobs, however at the moment it is extremely difficult to predict the future of technology and the countless opportunities it could provide. The future generations entering the workforce need to increase their skill belt in order to compete with AI or algorithms. But AI (currently) cannot replicate human skills such as critical thinking, managing and recognising emotions. These are skills which enhance jobs which require teamwork. AI has some other very big flaws such as high cost in installation, maintenance and the countless amounts of updates to prevent malfunction but in a lot of cases it can be beneficial to the company and its employees as it removes the need for people to waste time and productivity on tasks which an AI can easily complete. In the far future AI will become more competent than humans at jobs and work in general but in our lifetime AI will not render all human labour useless. For now it will take a large proportion of low skill work but a lot of white collar work will just be improved upon but not replaced by AI. The way our society works is based on consuming and to be able to consume you have to have money and to get money you have to earn through working in a job, so if nobody can make money how will the economy continue to prosper?
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Word of Advice to Our Trainees
There is general advice and exam specific advice (highlighted text has hyperlinks).
General Advice
This applies to preparing for local practice in Singapore. This has a slightly American slant (unfortunately the exams you will be sitting are British and Australian).
Refer to your JCST Seamless Programme Medical Microbiology Training Syllabus and use this as a checklist. Literally tick off each item as you go so that there are no gaps in your training experience.
During your lab training you will be used to seeing tests as individual items. However you must get your head round to seeing things also from the clinician’s perspective. For a patient presenting with a particular syndrome which battery of tests are appropriate for that individual patient? Even for a single pathogen (particularly with viruses), there may be a choice of different tests that can be used. Which are most appropriate for that particular situation? This is one of the characteristics that distinguishes medical student knowledge from that of a microbiology trainee.
I suggest right at the beginning of training to get the fundemental cliinical perspective in place by reading Infectious Diseases A Clinical Approach by Yung et al. This is book is simple enough to be read in a fortnight. (Update Jan 2020: The new kid on the block is Comprehensive Review of Infectious Diseases by Spec A et al-which comes with an ebook with over 400 nicely written MCQs-unfortunately it probably can’t be finished in 2 weeks).
Please get yourself a microbiology textbook and systematically read it from cover-to-cover. The most appropriate at time of writing is the latest edition of Koneman’s Color Atlas and Text book of Diagnostic Microbiology. You should try to complete reading this book within your first year of training.
This will not be enough for Virology. Some may find Khare Guide to Clinical and Diagnostic Virology too simple but I think reading it cover-to-cover is still useful for the 1st year trainee. For subsequent years you will need to read selectively Loeffelholz Clinical Virology Manual for the lab perspective and maybe dip into Richman Clinical Virology for the clinical approach.
The following websites are useful
For parasitology
CDC DPDx
Gorgas Course Case of the Week
CREEPY DREADFUL WONDERFUL PARASITES
For mycology
Mycology Online
One of the first things you should acquaint yourself with is the local lab, and hospital, biosafety and disinfection/sterilization policies. For lab biosafety the freely available BMBL should suffice as a reference.
In practice, you can expect to give a lot of advice on specimen collection so please familiarize yourself with our Pathology Handbook (and know where to find it). For reference you should look at A Guide to Specimen Management in Clinical Microbiology.
You should also familiarize yourself with our lab manuals (and those of the labs you visit when posted out-ask yourself why they are doing things differently from us).
For technical details you should also refer to the Clinical Microbiology Procedures Handbook.
There are 2 books you will always be consulting as references
Mandell, Douglas, and Benett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases
Use this when you are following up interesting cases or building up your case portfolio
ASM Manual of Clinical Microbiology
Not to be used as your primary textbook!
The most useful journals to read are the Journal of Clinical Microbiology, Clinical Microbiology Newsletter and Clinical Microbiology Reviews.
Please also look at the Cumitech Collection and the CLSI documents.
For infection control I like Lautenbach Practical Healthcare Epidemiology. For more details you should be keeping up to date with journals like Infection Control and Epidemiology and the Journal of Hospital Infection.
By the time you start preparing for the Part 2 exams you should be dealing with, and reading up on, management issues.
You should have helped trouble shooting of QA failures, and be familiar with the other CLSI documents that are relevant to lab practice but not microbiology specific. You should have been involved in at least one CAP accreditation inspection and should have passed the CAP inspector course itself.
The most useful lab management textbooks are
Garcia Clinical Lab Management
Wagar Lab Administration for Pathologists
Varnadoe Medical Laboratory Management and Supervision
But you should also familarize yourself with the local regulations governing labs and your hospital policy for issues like staff discipline etc…
Royal College of Pathologists (RCPath)
Look up the FRCPath training syllabus and tick off items to make sure you have covered all the ground. Look up past-year exams so that during your training you get a sense which lab situations you encounter are likely to come up as exam topics.
The principle of the postgraduate exams is they test you for your suitability to be a consultant. Because local practice is more lab-based, you will have to simulate the UK training environment.
A UK trainee may handle 5-10 positive blood cultures a day followed by a ward round that covers another 5 patients with infection issues like osteomyelitis or septic arthritis, AND a daily ICU round. They may encounter an infection control scenario every 1-2 weeks (needlestick, outbreak, staff exposure etc…). For this, they are giving specific advice including further investigations, antibiotic choice, dosage (remember they are also advising on therapeutic drug moniitoring for vancomycin and aminoglycosides), infection control measures, etc…
Even though we do not manage patients like they do in the UK you should build up your own personal case portfolio based on what you report in the lab. Do not stick to the minimum requirement in the syllabus! Actively follow up these cases and imagine how you would manage these patients if you were the doctor-in-charge.
Get the Oxford Handbook of Infectious Diseases and Microbiology, read it cover-to-cover and use it to guide your ‘management’. How would you adjust the dose for renal imparment? What alternative would you use if there was penicillin allergy?
UK trainees often refer to Kucer’s The Use of Antibiotics when finding out details about antibiotics so you should read it up for at least the common antibiotics that are commonly used (in Singapore and the UK).
Read through the editorials and guidelines in the Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy going back at least 2 years (esp guidelines and new antibiotics). Check out the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy website.
Two books I find useful for selective reading are
Fungal Infection: Diagnosis and Management by Richardson and Warnock.
Lecture Notes on Tropical Medicine by Beeching and Gill
I have not got a copy of the Communicable Disease Control and Health Protection Handbook yet but it looks like it could be handy (Update Jan 2020: I have a copy now and it is useful for RCPath trainees).
You should also construct scenarios for infection control and outbreak management to supplement your actual experience. A lot of exposure management (e.g. VZV, measles, hepatitis B) can be found in the Green Book.
Go through the IPC in 5 videos. This is part of the trainee education program. Every UK trainee knows this material. So you should too.
Read through the editorials and guidelines in the Journal of Hospital Infection going back at least 2 years. Check out the Hospital Infection Society website.
You should subscribe (or have access ) to the UKNEQAS Microbiology Interpretive Comments.
You will also need to pretend that you are a Consultant Microbiologist practicing in the UK. Unlike the US, there is a lot more central control in the UK so all UK consultants receive and are expected to comply with the same set of guidance documents.
I could create my own list of useful websites where such documents may be found but microregistrar has already done it for me. PHE, HTM (e.g. dealing with water supply in hospitals) are particularly relevant. I don’t know if questions ever came out from the DH Building Notes, but it may be useful to know what relevant documents are in there (like HBN 00-09).
Don’t forget to scour the RCPath website and even read the bulletin going back 2 years for any material that may be relevant (like audit reports, documents or discussion of current college issues).
And don’t forget the UK follows ISO15189 for lab accreditation so you probably should know a bit about UKAS (How would you perform measurement of uncertainty for a PCR test?).
In my opinion, the FRCPath is quite a straightforward exam, and paradoxically quite a difficult exam to pass at the same time. They are not likely to ask anything a District General Hospital Microbiologist will not encounter, so no exotic bugs here. If you are fully involved in daily lab activities you may even be better prepared to sit the exam purely on accumulated experience rather than mugging standard textbooks. But as you can see from this list-if you do not know what to spend your energy on, fail to ensure you accumulate appropriate experience, or if you do not read the right material you could end up with close to zero exam-specific knowledge.
(Update Jan 2020: Infectious Diseases, Microbiology and Virology: A Q&A Approach for Specialist Medical Trainees is a new MCQ book which is useful for RCPath candidates. I am not that keen on the format of the MCQs (prefer Spec et al) but the selection of topics will give you some idea of the domain knowledge college examiners are looking for).
Royal College of Pathologists of Australasia (RCPA)
The RCPA seems to have changed to be more similar to the RCPath in the sense that they are now testing more practical consultant competence and less esoteric knowledge.
Therefore go through the same process as for the FRCPath.
Investigate the RCPA website for the training syllabus and other issues that Australian pathologists are currently grappling with. For Part 2, relevant issues may not be obviously microbiological (like how do you handle bullying in the lab?). The RCPA actually put a lot of training material onsite including the National Microbiology Webinar series (need to be RCPA registered trainee for access). It goes without saying you should go through all of them.
Be aware they have their own Antibiotic Guidelines Book.
Other Australia specific websites (equivalent to those mentioned for RCPath) are
Australian Committee on Safety and Quality in Health Care
Department of Health
NATA
NHMRC
Australian Immunisation Handbook
Australian STI Guidelines
SA Health Antimicrobial Guidelines
ASHM testing portal
And like their marsupials, Australian microbiology has its own distinctive flavour. e.g. Legionella longbeachae, Cryptococcus gattii, Mycobacterium ulcerans, Hendra virus etc... So be familiar with what’s happening Down Under.
Hmmm...this turned out much longer than I expected. Hope it won’t scare off any prospective trainees...
P.S. There is also the SGH Department of Microbiology training Handbook.
1 note
·
View note
Text
83 Things That Blew Our Minds in 2018
Most “Himalayan” pink salt is from the Punjab area of Pakistan, not the actual Himalayas.
Hippos poop so much that sometimes all the fish die.
In addition to the supermassive black hole at its center, the Milky Way galaxy may be home to thousands of smaller black holes, invisible to even our finest scientific instruments.
There’s a parasitic fungus that doses cicadas with the hallucinogen found in shrooms before making their butts fall off.
The Arctic Ocean is now so warm that its floating sea ice can melt even during the coldest, darkest times of the year.
You can make thousands of dollars a week charging electric scooters.
When your eyes look right, your eardrums bulge to the left, and vice versa. And the eardrums move 10 milliseconds before the eyes do.
More than 2 million years ago, well before Homo sapiens evolved, one of our ancient-human relatives lived in what is now China.
Women who have had six to 10 sexual partners in their lives have the lowest odds of marital happiness, according to one study.
When Chicago’s Shedd Aquarium opened in 1930, the inland aquarium had to ship a million gallons of ocean water by train from Key West, Florida.
Twitter is the preferred social network for nudists to meet and connect online.
The population of older adults who misuse opioids is projected to double from 2004 to 2020.
The data economy didn’t begin with Google or Facebook in the 2000s, but with electronic information systems called a relational databases, first conceived of in 1969.
At their most voracious, wildfires can grow 100 feet high and consume a football field of forest every second.
People with autism are 10 times as likely to die by suicide as those in the general population.
The number of exclamation points now necessary to convey genuine enthusiasm online is, according to most internet users, three.
An “ice tsunami” killed a herd of musk oxen in February 2011 and kept their bodies perfectly entombed for seven years.
Ten thousand years ago, the people who lived in Europe had dark skin and blue eyes.
Facebook sent huge volumes of data about you and your friends to millions of apps from 2007 to 2014, and you have no way to control—or even know—how that information gets used.
A fishing cat is a water-loving cat species that lives in swamps, quacks like a duck, and dives from riverbanks to snag unsuspecting fish.
Astrology is experiencing a resurgence among Millennials, fueled by meme culture, stress, and a desire for subjectivity in an increasingly quantified world.
In the beginning of 2018, Amazon had 342 fulfillment centers, Prime hubs, and sortation centers in the United States, up from 18 in 2007.
Ivy League universities took nude photos of incoming freshman students for decades.
Some fundamentalist Christian groups think the spread of implantable technology is a key sign of the impending apocalypse.
The shopping mall put a cap on consumerism as much as it promoted it.
Bees stop buzzing during total solar eclipses.
The scientist who advised the production team of Interstellar made so much progress on his research in the process that it led him to publish multiple scientific papers.
High fibrinogen content can help a blood clot stay in a shape like putty—even if it gets violently coughed up.
Many butterflies in the nymphalid group can hear with their wings.
Some scientists think the reason you want to squeeze or nibble on a particularly cute baby is to snap your brain out of the euphoria that cuteness can summon, making you able to tend to the baby’s needs.
In the fourth quarter of last year, 25 percent of all new office space leased or built in the United States was taken by Amazon.
The first scooter was invented in 1990 by a guy who really wanted a bratwurst.
The streets of Boston carry an average of four gas leaks a mile.
In August, Oxford University’s Said Business School came up with a clever way for homeless people to receive cashless donations: Donors could scan the barcodes on homeless people’s lanyards to send them money.
Don’t worry if you forget all the facts you read in this article by tomorrow—that’s normal.
Many doctors have difficulty accessing the health records of patients treated previously at another facility; less than half of hospitals integrate electronic patient data from outside their system.
The original indigenous American dogs are completely gone, and their closest living relative isn’t even a dog—it’s a contagious global cancer.
Donald Trump can’t really send a message directly to your phone. In fact, the president’s ability to address the nation directly in a time of crisis, available since the 1960s, has never been used.
In 1995, a man in Germany realized his pet crayfish was cloning itself. Clones of that crayfish have now spread all over the world.
Four hundred years after Galileo discovered Jupiter’s largest moons, astronomers are still discovering some tiny ones.
The fastest someone has ever hiked all 2,189 miles of the Appalachian Trail is 41 days, seven hours, and 39 minutes. That averages out to roughly two marathons a day.
The lifespan of a meme has shrunk from several months in 2012 to just a few days in 2018.
Elon Musk’s $20 million SEC fine might make his ill-advised “funding secured” tweets the most expensive ever.
Thousands of horseshoe crabs are bled every year to create a miraculous medical product that keeps humans alive.
Single-celled microorganisms can survive in lab conditions that simulate the icy environment of Saturn’s moon Enceladus.
Only 10 major hurricanes have ever made landfall along the Southeast Atlantic coast, if you don’t count Florida.
Animals that live in cities are sometimes found to outperform their rural counterparts on intelligence tests.
Jupiter’s famous Great Red Spot is shrinking.
The paleontology consultant for Jurassic Park had a Tyrannosaurus rex eat a doppelgänger of another researcher with whom he had academic beef.
Some people think tennis balls are green while others think they’re yellow, and the disagreement has a lot to do with how our brains perceive color.
Conservatives tend to find life more meaningful than liberals do.
It’s easier for spacecraft to leave the solar system than to reach the sun. Thanks, physics.
Despite giving away hundreds of millions of dollars to charity, the Microsoft co-founder Paul Allen was worth $20 billion when he died, 48 percent more than when he signed the Giving Pledge in 2010 and promised to give away at least half his wealth.
China consumes 28 percent of the world’s meat—with the average resident eating 140 pounds a year.
Europa, a moon of Jupiter, may be covered in 50-foot-tall blades of ice.
You can reconstruct a pretty decent record of historical whaling intensity by measuring the stress hormones in the earwax of a few dozen whales.
Doing a good deed—or even imagining doing a good deed—can boost an athlete’s endurance by reinforcing his or her sense of agency in the world.
A science adviser on Stargate: Atlantis imagined a fictional astronomical phenomenon called a binary pulsar system for the show. Years later, such a system was found in real life.
The lowercase g in Google’s original logo is really, really weird.
Sixty percent of gun deaths in 2017 were suicides.
From 1984 to 2015, the area of forest in the American West that burned in wildfires was double what it would have been without climate change.
An astrologer came up with the phrase “super blue blood moon” to describe a celestial event that’s much less scary than it sounds.
The Cambridge Analytica scandal caused 42 percent of Facebook users to change their behavior on the platform, according to a survey conducted by The Atlantic. Ten percent of those people deleted or deactivated their accounts.
In the absence of federal regulation or good research about how skin-care products work, communities of citizen scientists have started compiling pretty decent resources.
The figure-eight trajectory flown by the Apollo moon missions was the very same path followed by fictional astronauts in a classic silent film from 1929, Woman in the Moon.
After one year in America, just 8 percent of immigrants are obese, but among those who have lived in the U.S. for 15 years, the obesity rate is 19 percent.
There’s a spider that makes milk.
Goats love to feast on weeds, and you can rent dozens of them to landscape your lawn.
Some people have a bony growth on the back of their heel, called a pump bump, that makes it hard to wear pumps and other kinds of dressy shoes.
Astronomers can still detect ripples in the Milky Way caused by a close encounter with another galaxy hundreds of millions of years ago.
China built its rocket-launch facilities deep inland to protect them during the Cold War, but decades later it actually makes launching rockets into space more dangerous.
The folks who make Piaggio scooters hope you might buy an R2D2-like cargo robot to haul a case of Aperol home from the market.
Shifting the pitch of an audio recording can make it sound like an entirely different word.
Kids under the age of 8 spend 65 percent of their online time on YouTube.
A reservoir of liquid water may lurk just a mile beneath the ice-covered surface of Mars’s south pole.
When people overdose in public bathrooms, many service workers become the unwitting first line of medical responders.
Some people think that quantum computing will bring about the end of free will.
Mouse urine is a major cause of asthma for poor kids in Baltimore.
The House of Representatives’ longest-serving member, Alaska’s Don Young, was first elected to his seat after his opponent died.
In September, Hurricane Florence dropped about 18 trillion gallons of rain over the Carolinas—enough water to completely refill the Chesapeake Bay.
Europe suffered its worst carbon dioxide shortage in decades (think of the beer and the crumpets!) because of a closed ammonia fertilizer plant. Yes, these two things are related.
Americans spent $240 billion on jewelry, watches, books, luggage, and communication equipment such as telephones in 2017, twice as much as they spent in 2002, even though the population grew just 13 percent during that time.
People get more colds in winter because chilly temperatures make it easier for microbes to reproduce inside your nose.
Article source here:The Atlantic
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Navigating the Path to Medical Success: NEET Classes in Pune
Introduction
The National Eligibility-cum-Entrance Test (NEET) is the gateway to a fulfilling career in the medical field in India. Every year, thousands of aspirants vie for a limited number of seats in prestigious medical colleges across the country. To secure admission to their dream institutions, students often turn to coaching centers for guidance and preparation. Pune, with its rich educational heritage, has emerged as a hub for NEET coaching, offering a plethora of options for aspiring doctors. In this article, we will delve into the world of NEET classes in Pune, exploring what makes the city a favorable destination for medical aspirants.
Pune: A Thriving Educational Hub
Pune, often referred to as the "Oxford of the East," is renowned for its educational institutions and rich academic history. Home to prestigious universities and colleges, the city has consistently produced top-notch professionals and scholars. This academic ecosystem has naturally extended to NEET coaching institutes, making Pune an attractive destination for aspiring doctors.
Quality Coaching Centers
Pune boasts a multitude of NEET coaching centers, both big and small, that cater to the diverse needs of students. These institutes offer a structured curriculum, expert faculty, and state-of-the-art facilities. The quality of coaching in Pune is often compared to that of major educational hubs like Delhi and Kota, making it a sought-after destination for NEET Preparation Course Structure.
Expert Faculty
One of the crucial aspects of NEET coaching is the quality of teaching. Pune's NEET coaching centers are known for their highly qualified and experienced faculty members who guide students through the intricacies of the NEET Course Syllabus. These mentors provide personalized attention, clearing doubts, and ensuring that students grasp the concepts thoroughly.
Comprehensive Study Material
NEET requires a comprehensive understanding of subjects like Physics, Chemistry, and Biology. Pune's coaching centers provide meticulously designed study material that covers every aspect of the syllabus. These materials are updated regularly to align with the latest NEET patterns, ensuring that students are well-prepared.
Mock Tests and Practice Papers
Success in NEET often hinges on rigorous practice and effective time management. Pune's coaching institutes conduct regular mock tests and provide ample practice papers to help students fine-tune their exam-taking skills. These tests simulate the real NEET exam environment, enabling students to manage their time efficiently and reduce exam anxiety.
Individual Attention
Unlike larger cities where batch sizes can be overwhelming, Pune's NEET coaching centers often offer smaller batch sizes. This allows for more personalized attention, ensuring that students' doubts are addressed promptly and their progress is closely monitored.
Proven Track Record
Pune has a history of producing NEET toppers and successful medical professionals. Many NEET coaching centers in the city proudly showcase their track record of students who have secured admissions in prestigious medical colleges. This success rate speaks volumes about the effectiveness of the coaching institutes in Pune.
Competitive Environment
Studying in Pune provides students with the opportunity to immerse themselves in a competitive environment. Interacting with like-minded peers who are equally driven can be a motivating factor for many aspirants. The healthy competition pushes students to excel and perform their best.
Access to Educational Resources
Pune's educational infrastructure extends beyond coaching centers. The city is home to well-equipped libraries, research centers, and educational resources that can be immensely helpful for NEET preparation. Students can access a wide range of reference materials and journals to enhance their knowledge.
Choosing the Right NEET Coaching Center in Pune
While Pune offers a plethora of options for NEET coaching, selecting the right institute is paramount to success. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a coaching center:
Reputation: Research the coaching center's reputation and track record. Read reviews, talk to current or former students, and check the success rate of the institute.
Faculty: Look for institutes with experienced faculty members who are experts in their respective subjects.
Study Material: Examine the study material provided by the coaching center to ensure it is comprehensive and up-to-date.
Batch Size: Consider the batch size to ensure that you will receive adequate attention from the faculty.
Location: Choose a coaching center that is conveniently located and easily accessible from your home or hostel.
Infrastructure: Assess the institute's infrastructure, including classrooms, libraries, and labs.
Fee Structure: Compare the fee structure of different coaching centers and ensure it aligns with your budget.
Conclusion
Pune's thriving educational ecosystem, coupled with the presence of quality NEET coaching centers, makes it an ideal destination for aspiring doctors. With expert faculty, comprehensive study material, and a competitive environment, students in Pune are well-prepared to face the NEET exam confidently. However, success ultimately depends on an individual's dedication and hard work. Therefore, while NEET coaching in Pune can provide the necessary guidance and resources, students must also put in the effort required to achieve their medical aspirations.
0 notes
Text
Within vitro review in the photograph(geno)toxic body related to Encorafenib, a new Tyrosine Kinase inhibitor
Several; 17 to be able to Twenty four). A couple of individuals essential the conversion process to TKR: one pertaining to growth of horizontal pocket osteo arthritis and something for infection. Implant tactical with 5yrs had been 93% (95% CI Eighty three for you to One hundred). All but one particular individual described being pleased with the procedure. The outcome wasn't substantially relying on grow older, sex, femoral or perhaps tibial tube position, or if the method has been performed from one- or even two-stages. In overview, ACL recouvrement and Oxford UKR provides achievement inside sufferers along with end-stage MCOA secondary in order to ACL deficiency.Background: A lot of people along with schizophrenia notice a profound debt in worldwide psychological capacity, which is related to very poor functional outcomes. Traditionally, the standard of determining neurocognitive disabilities is among substantial neuropsychological power packs which are labour-intensive. The existing study reviewed whether a shorter neurocognitive evaluation (BNA) tool might efficiently calculate worldwide neurocognition and further analyzed its medical Selleck Encorafenib power. Strategies: Your truth and scientific electricity of an BNA that takes about 10 mm to manage had been looked at versus an entire neuropsychological battery pack that can take roughly Ninety minimum to provide in the huge along with heterogeneous test associated with 1303 individuals using schizophrenia. Final results: The particular BNA discussed 76% in the alternative inside global neurocognition from the total taste as well as always been constant throughout subsamples stratified simply by medical characteristics (elizabeth.g., severity of psychopathology) as well as in randomized re-sampling simulations. The 2 things that made up the particular BNA ended up the letter-number sequencing test, a step of doing work storage Selleckchem Gemcitabine , and the digit-symbol check, a pace regarding digesting speed. Following, possibly more importantly, the particular BNA and total neuropsychological battery power were associated with signs and symptoms and also practical standing into a equivalent diploma in univariate and multivariate regression types; additionally, each devices were sensitive to longitudinal treatment method linked change to an identical degree DNA . Results: Your BNA will be able to rapidly, easily, and also validly determine world-wide neurocognition within schizophrenia. The BNA had been associated with crucial specialized medical outcomes into a equivalent degree as being a total intellectual battery power. This tool offers specialists and researchers a way to examine international neurocognitive impairments with no demanding considerable neuropsychological assessment. (D) This year Elsevier Ltd. All legal rights set-aside.Qualifications: Abnormal misfolded tau proteins are the driving force associated with neurofibrillary deterioration throughout Alzheimer's. It is often revealed in which tau oligomers participate in a vital role in the development regarding intra-cellular neurofibrillary knots. These are intermediates in between dissolvable tau monomers along with insoluble tau filaments and they are alleged contributors in order to illness pathogenesis. Oligomeric tau may be released in to the extracellular space and spread all through the brain.
0 notes
Text
Why Does Cannabis Work for So Many Different Health Conditions?
By M. Carroll on August 12, 2021Health

The human body continues to amaze scientists. No one has the final answer to anything regarding human physiology, neurology, respiratory, and other systems. Any successful discovery only opens more doors and raises more questions.
Illness has been with us for eons and eons. Some illnesses even evolve and morph. And, since the earliest times, clans and tribes trusted certain people to fix and cure. Until the scientific method came along in the 15th-century, you could not find a universal and transferable solution to problems. The scientific method would launch centuries of development in anatomy, botany, genetics, and more.
But, the scientific method also pushed aside a lot of history, the potions and potables left to priests/priestesses, shamans, wizards, and alchemists. Left to ply their arts on the edge of society, their discoveries are best remembered by a verbal tradition, a history of legends and anecdotes.
As with so many of the right things they did were the discoveries of cannabis, peyote, and other natural resources. Add to that the fact that the pursuit of the scientific method depends on big money, and you find biased motives to keep research into these resources limited.
History makes way for Dr. Mechoulam!
The organic chemistry genius, Raphael Mechoulam, emigrated with his family from Bulgaria to Israel in the late 1940’s. A graduate of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, he completed his doctoral studies at Rehovot’s Weizmann Institute and postdoctoral work at Manhattan’s Rockefeller Institute. A member of the Israel Academy of Sciences, Dr. Mechoulam is professor at the Hebrew University, an eminent Israeli and world genius.
What he did in the 1960’s was open the treasure that is cannabis and ready it for the kind of scientific inquiry that had left it in the shadows for so long. Basically, he led a team to synthesize THC (Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol). And, with colleagues, he isolated anandamide and 2-AG, the first endocannabinoids isolated for study.
What comes of this?
Among the body’s many systems is the endocannabinoid system. It runs broadly throughout the human anatomy. It is less independent and differentiated than you might imagine the respiratory system or renal system. It is layered and ubiquitous. Robert Weber explains the endocannabinoid system in a short video.
You might visualize it as a chain of neurons. At the end of each neuron lies a set of receptors that accept transmissions from the previous neuron. In healthy people, the system runs smoothly with the receptors taking just the right amount of transmission and passing it on. If for any reason, like injury or infection, the system is interrupted or upset, the receptors fail at their job, and that registers as pain.
Because of the spread of the endocannabinoid system, that disruption can be felt as a localized disruption like a migraine. Or, it can involve wide-ranging webs as in fibromyalgia and chronic back pain.
Other scientists created the pharmaceutical family of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRI) that fight depression by restoring the harmony in the distribution of serotonin. But, the endocannabinoid system is more complex and less “easily” isolated.
And, because it’s everywhere –
Because of the endocannabinoid system is so present in all parts of the brain and body, it’s connected to more ailments and conditions than other systems. Various state laws recognize as many as 40 conditions as eligible for cannabis treatment.
The Illinois Department of Health lists the following debilitating conditions:
Agitation of Alzheimer’s Disease
Chron’s disease
Hydromyelia
Nail-patella syndrome
Residual limb pain
Spinocerebellar ataxia
HIV/AIDS
CRPS
Interstitial cystitis
Neurofibromatosis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Syringomyelia
ALS
Dystonia
Lupus
Parkinson’s disease
Seizures (epileptic)
Tarlov cysts
Arnold-Chiari Malformation
Fibrous dysplasia
Multiple Sclerosis
Post-concussion syndrome
Severe
fibromyalgia
Tourette’s syndrome
Cancer
Glaucoma
Muscular dystrophy
PTSD
Sjogren’s syndrome
Traumatic brain injury
Causalgia
Hepatitis C
Myasthenia gravis
Reflex sympathy disorder
Spinal cord disease
Cachexia/wasting syndrome
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
Hydrocephalus
Myoclonus
Post-concussion syndrome
Spinal cord injury
Cannabis research has taken two directions. The first is to use or emulate cannabis elements or derivatives in the manufacture of medical pharmaceuticals. The British company GW Pharmaceuticals has committed to finding healing solutions in cannabis. Their products include Sativex®, a treatment of spasticity associated with multiple sclerosis and childhood epilepsy has been approved in 29 countries – outside the United States.
GW also has a pipeline that includes Epidiolex® in Phase III testing for treatment of Dravet Syndrome and Lenox-Gastaut Syndrome. Other drugs in Phase I and II include care for epilepsy, autism spectrum disorders, neonatal hypox-ischemic encephalopathy, and glioma.
The University of California – San Diego has established its Center for Medicinal Cannabis Research, where studies are now underway, including:
Effect of Cannabis and Endocannabinoids on HIV Neuropathic Pain
A Randomized, Controlled Trial of Cannabis in Healthy Volunteers Evaluating Simulated Driving, Field Performance Tests and Cannabinoid Levels
A Randomized, Cross-Over Controlled Trial of Dronabinol and Vaporized Cannabis in Neuropathic Low Back Pain
According to CNBC.Com, Oxford University, “The oldest university in England will be teaming up with private equity company, Kingsley Capital Partners who will provide up to £10 million ($12.36 million) in initial investment, which will be funded through its new biopharmaceutical firm Oxford Cannabinoid Technologies (OCT).”
The Associated Press reports, “University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences plan a 5-year study to examine why synthetic compounds — such as K2 and Spice — are more toxic than marijuana.”
And, “a 2015 study published by the National Bureau of Economic Research, a non-partisan think-tank, "[S]tates permitting medical marijuana dispensaries experience a relative decrease in both opioid addictions and opioid overdose deaths compared to states that do not."
The preceding projects are often tied to and funded by pharmaceutical interests which does not diminish their value.
But, the second direction is to study the effects of medical marijuana. Without financial support for such research in the U.S., little is happening in this area. We are left with anecdotal history. It’s not scientific theory, but there is value in real world and real-time experience.
This has been driven lately by the potential of the burgeoning canna-economy. Breeders, farmers, harvesters, and purveyors need verification for the claims their marketing makes. An increasingly populated market will govern economic success as educated and informed consumers. History knows what science needs to prove: why cannabis works for so many different health conditions!
1 note
·
View note
Text
Could the VR (the product) be used outside of gaming?
VR is still a very new piece of technology, with many of its concepts and possibilities are still being developed. Whilst it benefits the gaming community and is helping to advance gameplay; could it have other applications in other branches of our society.
Medical applications?
Remote training?
youtube
VR could be used to train people in the basic first aid training without the need to book sessions and sit through hours of training sessions etc. The process puts the user in a “real-life” situation where an individual needs first aid, and takes them step-by-step through the process it would take to save a life until an ambulance can arrive.
This can be more effective than using ‘Annie’ during training as it simulates a life or death situation that will be taken more seriously than a doll in a utility room of a community hall. This also means practitioners can spend more time in the field or doing their jobs as opposed to spending hours training others.
Surgery practice for students to practice on - as opposed to the classic dolls?
vimeo
A simulation can also be used to train young doctors as this lessens the risk of misdiagnosing a real patient as well as reduces the risk during times such as these where you could come into contact with a virus.
The simulation tests the user throughout the process to check as the student checks for patient history, completes eye exams, rashes/marks, respiratory issues, or a plethora of other signs or signals as to what the issue is with the patient. It’s a good way of training students (possible university students) from their own homes.
Educational applications?
For children with learning difficulties?
Children with learning difficulties (such as ADHD, Autism, Asperger's, and Dyslexia) may have great difficulty learning in the 'traditional method' which is taught in school (sometimes called "traditional pedagogy"). This method can be rather strict and rigid as it treats all students on the same level, whilst this is easier for the teacher, it may not benefit the children. The teacher will talk and relay information to students who will then record and remember what has been said, unfortunately, those who struggle to write - either with correct spellings or struggle keeping up with the speed of a teachers speech pattern - will lose half the information stated and struggle to recollect the complete statement of information. Children/adolescents can be provided with support such as a sit-in LSA (learning support assistant) to assist them within the classroom. This system does appear to work however many children - around 40% (The Guardian) - go undiagnosed for learning difficulties and will appear as though they are not listening or are not paying enough attention causing negative repercussions later. That is an issue for the system in place for diagnosing learning difficulties.
A more diverse method of teaching can be taught and spread throughout the education system which benefits ALL students as opposed to those who are neurotypical or the few diagnosed with learning difficulties. Some believe VR could be the necessary next step in classroom education.


"Pandemic safe" virtual classroom?
“Remote learning” is the latest teaching method due to the Pandemic forcing everyone to social distance and stay within their homes. Remote learning consists of occasional video calls with a class and teacher and weekly check-ins between the educator and their students with many of the learning having to be on an online platforms (exams have now become 24hr exams and all coursework must be submitted through Dropbox). Whilst we cannot resume our ‘normal’ routine of learning as of yet, there may be ways we can improve the current routine by using technology that can give us a classroom - with other students and teachers - through VR.
The technology would simulate a classroom - as close as we can get - as we would be able to interact with fellow students without putting anyone at risk. It would put faces to names and help us keep up a healthy balance of social interaction and focused learning.
Sites such as “ClassVR” offer an online classroom for schools to buy into or subscribe to which would allow students to interact with classmates as well as their teachers without putting anyone at risk. Students can choose avatars and type messages to each other during the class.
Teachers will be trained to use the platform as well - something that was not offered when we switches to remote learning, leaving many teachers out of their comfort zone with technology and unable to provide clear instructions or the best support to students.
This technology could also be carried over even after the restrictions are lessened, it could be used for field trips (meaning students who ordinarily wouldn’t be able to afford the trip or perhaps were ill on the day could still attend in one way or another).
It could also be used to help visualize concepts and ideas better. An example would be like that of our exhibition, to help students visualize the space provided for their work, they could be given a 3D map of the room to allow them a better idea of how to present/install artwork.
Relevant Links
- Virtual reality in autism: state of the art; M. Bellani, L. Fornasari, L. Chittaro and P. Brambilla.
- Language Learning in Virtual Reality Environments: Past, Present, and Future
- Oxford Medical Simulator
- Mencap
- Educational VR & Remote learning at home
- ClassVR
- AR VR
0 notes